In the digital world, security is a top priority for individuals and organizations alike. As cyber threats evolve, so do the methods to counteract them. One-time passwords (OTPs) have become a cornerstone of modern security protocols, offering a layer of protection that traditional passwords cannot match. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of OTP, Time-based One-time Password (TOTP), and HMAC-based One-time Password (HOTP), shedding light on their importance in enhancing digital security.
The Critical Role of OTP in Multi-Factor Authentication
OTP is a unique code that is valid for a single transaction or login session. It’s a dynamic addition to a user’s static login credentials, forming a part of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA). MFA is a security system that requires more than one method of authentication from independent categories of credentials to verify the user’s identity for a login or other transaction.
Deep Dive into OTP (One-Time Passwords): How It Works and Why It Matters
An OTP is essentially a password that changes every time it is used, providing an additional layer of security. This transient nature of OTPs makes it incredibly difficult for unauthorized entities to gain access to sensitive information. The OTP system is designed to combat a variety of cyber threats, including phishing, man-in-the-middle attacks, and password theft.
The Generation of OTP: A Closer Look
The creation of an OTP is a sophisticated process that involves two primary inputs: a secret key (seed) and a moving factor. The seed is a static value, a secret known only to the user and the authentication server. The moving factor, however, varies with each OTP request. This could be based on a counter, time, or even a combination of both, depending on the type of OTP algorithm in use.
HOTP: The Event-Based Authentication Method
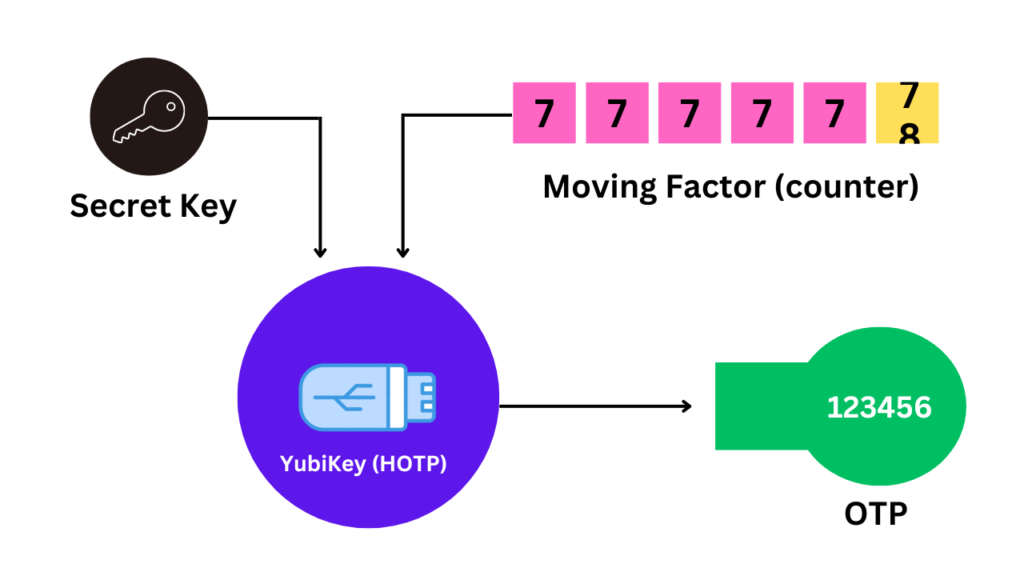
HOTP stands for Hash-based Message Authentication Code One-time Password. It is an event-based system where the moving factor is a counter that increments with each new OTP request. This means that the OTP remains valid until the next successful authentication event occurs. HOTP is ideal for situations where time is not a critical factor, and the user initiates the authentication process.
TOTP: The Time-Sensitive Approach
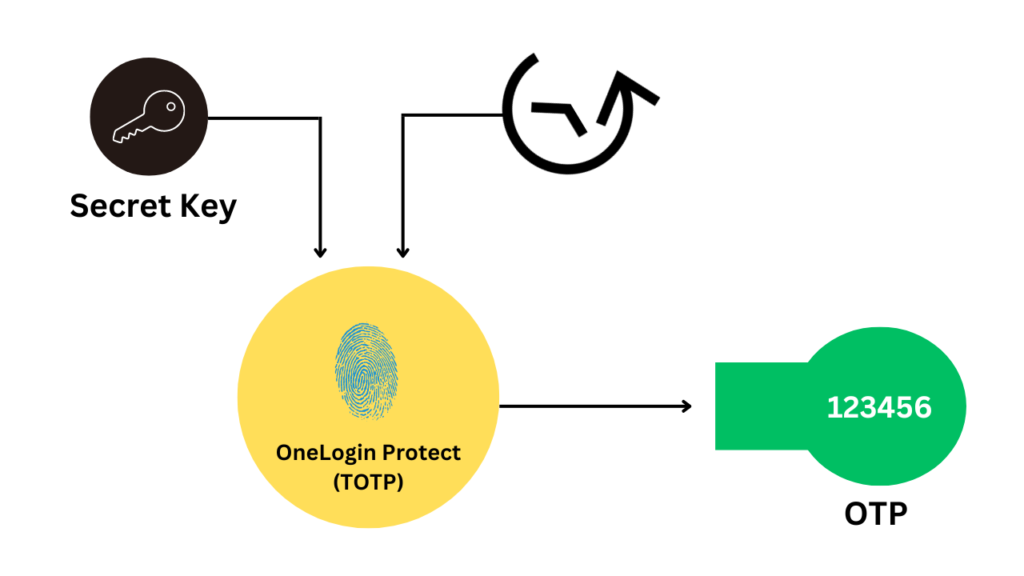
In contrast, TOTP or Time-based One-time Password relies on a time factor for the moving component. The OTPs generated by TOTP algorithms are only valid for a short period, typically 30 to 60 seconds. This method ensures that even if an OTP is intercepted, it would be rendered useless in a matter of moments, providing a robust defense against replay attacks.
The Advantages and Limitations of HOTP and TOTP
While both HOTP and TOTP enhance security, they have distinct advantages and limitations. HOTP’s flexibility lies in its lack of time constraints, allowing users to authenticate at their leisure. TOTP, however, promotes prompt authentication and reduces the window of opportunity for attackers to use a stolen OTP.
Implementing OTP, TOTP, and HOTP in User Experience
When integrating these authentication methods into user systems, it’s essential to consider the user experience (UX). A seamless UX is crucial for ensuring that security measures do not become a hindrance to productivity. OTP systems like OneLogin Protect provide a user-friendly interface that simplifies the authentication process while maintaining high security standards.
Conclusion: The Future of Digital Security with OTP, TOTP, and HOTP
As we move forward in the digital age, the significance of advanced authentication methods like OTP, TOTP, and HOTP cannot be overstated. They are vital components of a comprehensive security strategy, safeguarding personal and corporate data against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. By understanding and implementing these technologies, we can ensure a more secure and reliable digital environment for all.
While OTP, TOTP, and HOTP provide robust layers of security for authentication, it’s equally important to ensure that passwords themselves are stored securely. Understanding the mechanisms behind password storage can offer insights into the comprehensive security measures necessary for protecting sensitive data. If you’re curious about how passwords are safeguarded once they’re inside the database, we invite you to explore our detailed blog post on password storage best practices.