Web browsers are the gateways to the internet, allowing us to access, interact with, and navigate through the vast expanse of the World Wide Web. They are complex software applications that have evolved significantly since their inception, now offering a range of functionalities beyond merely displaying web pages. In this article, we will explore the intricate workings of web browsers by examining their main components and understanding how they collectively contribute to our online experience.
The User Interface: The Face of the Browser
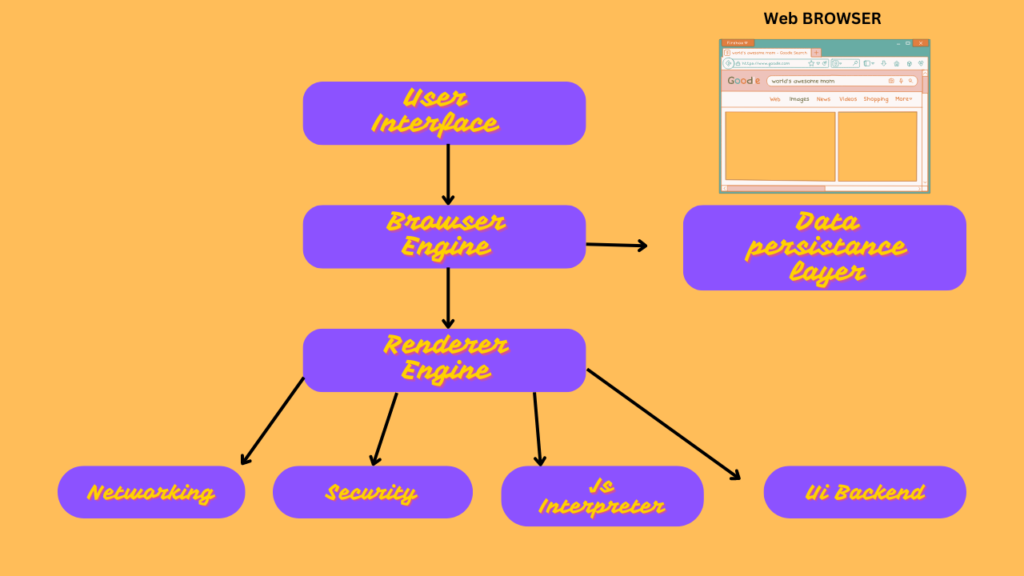
The user interface is the aspect of the browser that users interact with directly. It includes the address bar where URLs are entered, navigation buttons like back and forward, bookmarks, settings options, and extensions. This interface is designed to be intuitive, allowing users to perform a variety of tasks with ease. It’s the surface layer that masks the complex processes happening in the background.
Browser Engine: The Conductor of Operations
Sitting between the user interface and the rendering engine is the browser engine. This component acts as a mediator, interpreting user actions and directing the rendering engine accordingly. It plays a crucial role in managing the interaction between the user interface and the underlying processing of web content, ensuring that user commands result in the appropriate on-screen display.
Rendering Engine: Bringing Content to Life
The rendering engine is responsible for displaying requested web content. When a user requests a page, the rendering engine parses HTML and CSS files, converting them into visual representations on the user’s screen. Different browsers may use different rendering engines, which can affect how web pages are displayed. Some browsers even employ separate instances of the rendering engine for each open tab, isolating processes and enhancing stability and security.
Networking: The Communication Backbone
Networking is a fundamental component that handles all network operations within a browser. It manages HTTP requests, ensuring that when a user requests a page, the browser can retrieve it from the correct web server. This component is optimized for performance and security, using platform-specific implementations to maintain a consistent interface across different operating systems.
UI Backend: Drawing the Basic Elements
The UI backend is responsible for drawing basic widgets like combo boxes and windows. It abstracts the generic interface elements, utilizing the operating system’s user interface methods. This means that regardless of the platform, the browser can display its interface elements consistently, providing a uniform user experience.
JavaScript Interpreter: The Scripting Powerhouse
Modern web browsers come equipped with a JavaScript interpreter, which reads and executes JavaScript code embedded in web pages. This allows for dynamic interactions and functionalities within web pages, making them more than static displays of content. The JavaScript interpreter is a powerful component that supports the rich, interactive nature of today’s web applications.
Data Storage: The Memory of the Browser
Data storage is the component that allows browsers to store data locally on the user’s device. This includes cookies, cache, and various storage methods like FileSystem, IndexedDB, localStorage, and WebSQL. Persistent data storage is essential for functionalities like remembering user preferences, saving session information, and enabling offline access to content.
Security Module: Safeguarding the Browsing Experience
The security module of a browser is tasked with managing various security protocols and features, such as handling Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) and implementing sandboxing for tabs. Each browser has its own implementation of security measures, but they all work towards the common goal of protecting the user from malicious content and preserving the integrity of their data.
Read About: What is CAPTCHA? How It Safeguards Websites Against Automated Attacks.
Conclusion: The Symphony of Web browsers Components
In conclusion, web browsers are sophisticated tools composed of multiple, interdependent components. Each plays a specific role in delivering a seamless and secure browsing experience. From the user interface to the security module, these components work in harmony, much like a well-conducted orchestra, to translate user actions into interactions with the digital world. As technology continues to advance, we can expect web browsers to evolve further, introducing new features and capabilities that will redefine our interaction with the internet.
Understanding the complexity of web browsers is not just for tech enthusiasts or developers; it’s crucial for anyone who uses the internet. By knowing how browsers work, users can make informed choices about which browser best suits their needs and how to troubleshoot common issues. As we continue to rely on web browsers for an increasing number of tasks, appreciating their inner workings becomes all the more important.