In the ever-expanding landscape of cloud computing, Cloud Storage Solutions play a pivotal role in enabling businesses to efficiently manage and access their data. Among the myriad options available, three primary methods stand out: block storage, file storage, and object storage. Delving into their intricacies unveils unique features and functionalities tailored to diverse use cases and requirements.
1. Block Storage: Flexible and Performant
Overview of Block Storage
Block storage divides data into fixed-sized blocks, each treated as a separate unit with a unique address. These blocks are typically accessed as volumes, offering flexibility in storage management and utilization.
Characteristics and Use Cases
- Flexibility: Block storage provides unparalleled flexibility, allowing for direct application handling or setup as a file system, catering to diverse storage needs.
- Performance: With tight server integration, block storage delivers high performance, making it ideal for applications requiring rapid data access and processing.
- Limitations: However, block storage is restricted to a single server and lacks inherent sharing capabilities, posing scalability challenges for distributed environments.
2. File Storage: Streamlined File Management
Understanding File Storage
File storage builds upon block storage, abstracting files and directories at a higher level to simplify file management. It enables access via file-level network protocols like SMB and NFS, facilitating seamless sharing within organizations.
Advantages and Considerations
- Ease of Use: File storage offers a user-friendly interface, making it convenient for managing large files and directories across networks.
- Access Control: With file-level access control and support for access control lists (ACLs), file storage enhances security by allowing granular permission settings.
- Challenges: Despite its advantages, file storage may encounter difficulties in handling numerous small files efficiently, impacting performance in certain scenarios.
3. Object Storage: Scalable and Cost-Effective
Exploring Object Storage
Object storage represents a newer paradigm in cloud storage, focusing on scalability and durability for unstructured data. It stores data as flat objects accessible through RESTful APIs, offering a cost-effective solution for large-scale storage needs.
Key Features and Considerations
- Scalability: Object storage excels in scalability, making it suitable for storing vast amounts of data without constraints imposed by traditional file systems.
- Durability: With inherent redundancy and data protection mechanisms, object storage ensures high durability, minimizing the risk of data loss or corruption.
- Performance Trade-offs: While object storage provides cost-effective storage, its performance may lag behind block and file storage solutions, particularly in real-time applications.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution
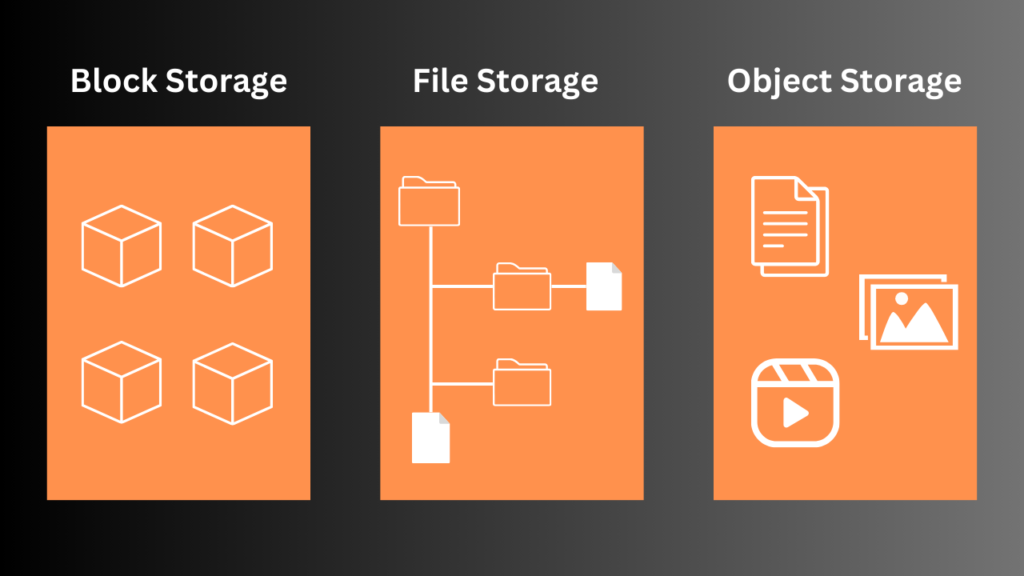
Each storage method—block, file, and object—brings its own set of advantages and considerations. Understanding your specific requirements and workload characteristics is essential in selecting the most suitable solution.
- For Performance-critical Applications: Consider leveraging block storage for its superior performance and flexibility, albeit with scalability limitations.
- For Collaborative Environments: File storage shines in scenarios requiring seamless file sharing and access control within organizations.
- For Scalable Data Storage: Embrace object storage for its scalability and cost-effectiveness, prioritizing durability and efficiency over real-time performance.
Read About: Demystifying Database Performance: A Deep Dive into Storage Engines.
Conclusion
In the dynamic realm of cloud storage, the choice between block, file, and object storage hinges on balancing performance, scalability, and cost considerations. By comprehensively understanding the characteristics and use cases of each storage method, businesses can optimize their data management strategies to meet evolving demands and unlock the full potential of cloud computing.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between block, file, and object storage?
- Block storage divides data into fixed-sized blocks and is accessed as volumes.
- File storage abstracts files and directories for easier management and sharing.
- Object storage stores data as flat objects accessible through RESTful APIs.
- Which storage solution is best for performance-critical applications? Block storage is ideal for performance-critical applications due to its superior performance and flexibility.
- What are the advantages of file storage in collaborative environments? File storage facilitates seamless file sharing and access control within organizations, enhancing collaboration.
- How does object storage excel in scalability and cost-effectiveness? Object storage offers scalability without constraints imposed by traditional file systems and is cost-effective for large-scale storage needs.
- What are the limitations of object storage in terms of performance? While object storage provides cost-effective storage, its performance may lag behind block and file storage solutions, especially in real-time applications.